Last Updated December 20th, 2021
What is the Arterial Blood Gas Analysis?
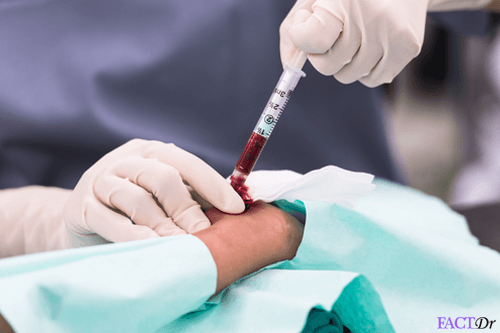
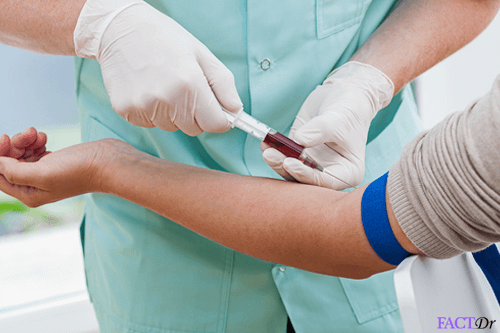
Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis is a blood test which measures the acidity (pH) and the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. The source of blood is an artery, unlike the routine blood tests which involve withdrawing blood from a vein.
Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis informs the physician about the activity of two systems- the respiratory system and the metabolic system. The organs concerned with these two vital activities are the lungs and the kidneys respectively. The endeavor of these two systems is to maintain the blood pH within the normal range.
What is blood pH?
It measures hydrogen ions (H+) in blood. The pH of blood indicates the acidity or alkalinity of the blood. The lower the pH, the more acidic the blood and vice versa. The normal pH of human blood is 7.35 to 7.45. On the pH scale, it can range from 0 (strongly acidic) to 14 (strongly alkaline). The pH is acidotic if pH <7.35 and is alkaline or basic if pH >7.45.
What are the indications for Arterial Blood Gas Analysis?
Arterial Blood Gas Analysis is generally a test performed in emergency care settings on critically ill patients. Acid-base interpretation is used to assess 4-primary acid-base disorders, which include the following:
– Respiratory acidosis (acute and chronic)
– Respiratory alkalosis (acute and chronic)
– Metabolic acidosis
– Metabolic alkalosis
Some of the indications for arterial blood gas analysis are-
– Any respiratory distress/failure (acute or chronic)
– Cardiac failure
– Liver failure
– Renal failure
– Hyperglycemic states
– Multiorgan failure
– Sepsis
– Burns
– Poisoning
– Assessment of response to interventions such as mechanical ventilation
How common are deaths by cardiovascular diseases in India?
Deaths from a heart attack and other cardiovascular diseases are on an all-time high in India. Many studies reveal that over 25% of all deaths in India are caused by heart diseases. Narrowing of arteries that supply blood to the heart can lead to several cardiac disorders and often result in sudden death. Even in global terms, stroke and heart failure are the #1 causes of deaths.
What are the contraindications of Arterial Blood Gas Analysis?
– Coagulopathy
– Severe atherosclerosis
– Infection/previous surgery or cutdown at site
– Decreased collateral flow
What does the Arterial Blood Gas Analysis measure?
Arterial blood gas analysis is not interpreted as positive or negative or as high or low. Instead, it provides the values of the following FIVE parameters.
– The partial pressure of oxygen– It is the pressure of oxygen in the arterial blood (dissolved in plasma) and is denoted by P02. In a healthy adult, its value is80-100 mmHg.
– The partial pressure of carbon dioxide -It is the pressure of carbon dioxide in the arterial blood and is denoted by PCO2. Its optimum value is 35-45 mmHg.
– Blood pH-The pH of blood indicates its acidity or alkalinity. The normal pH of human blood is 7.35 to 7.45.
– Bicarbonate (HCO3)- This is the form in which almost 90% of carbon dioxide in the blood is found. Bicarbonate acts as a buffer in the blood and helps maintain optimal pH. The normal value of bicarbonate in the blood is 22-28 mmol/L.
– Oxygen saturation- Denoted by sO2, it is the amount of oxygen that is bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Its value ranges from 95-100%.
How to prepare for Arterial blood gas analysis?
You should talk to your doctor in detail regarding your medical history.
Inform him if-
– You are allergic to any medicine.
– You are suffering from a bleeding tendency
– You are taking a blood thinner.
Do I need to fast before Arterial Blood Gas Analysis?
No fasting is required before an arterial blood gas analysis.
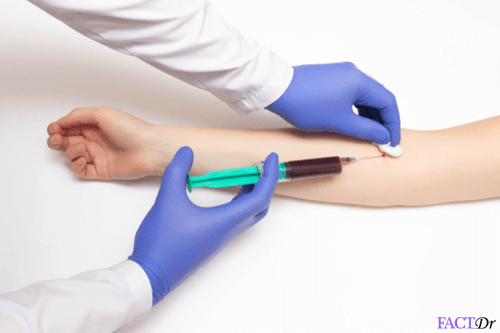
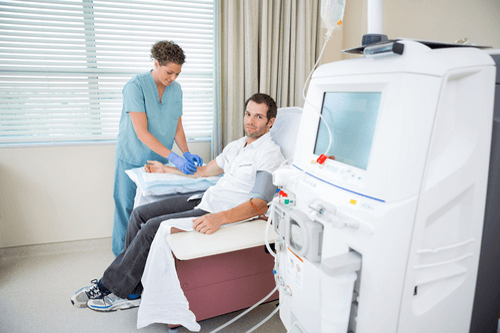
How is Arterial blood gas analysis performed?
Arterial blood gas analysis, as the name specifies, is a blood test. It uses blood withdrawn from an artery-the radial artery in most cases. It is of utmost importance to determine the viability of collateral circulation before invading radial artery.
Before the arterial blood gas test, your doctor may apply pressure to the arteries in your wrist for several seconds. The procedure, known as the modified Allen test serves the purpose of checking whether blood flow to your hand is normal.
An ABG kit is routinely used. Among other things, it contains 3-5 ml pre-heparinized syringe, 25-gauge needle, alcohol swabs, Iodine-based antiseptic swabs, Gauze pad, Cup or bag of ice and protective equipment for universal precautions.
If you are on oxygen therapy, the physician may turn off oxygen for 20 minutes before the blood test. This is called a “room air” test. If you have difficulty in breathing without the oxygen, the oxygen will not be turned off.
A local anesthetic is generally injected at the puncture site as it is a painful procure. Local anesthesia with epinephrine-free lidocaine is commonly used.
The physician withdraws 2-3 ml of blood from the radial artery (located on the thumb side of the wrist), takes out the needle quickly and applies the gauze pad using firm pressure at the site for at least 5 minutes. This is done in order to prevent the formation of a hematoma at the site of the arterial puncture. The sample can be refrigerated for a maximum of 24 hours.
How long does it take for the result of arterial blood gas test to be out?
The result is usually obtained in fifteen minutes.
How to interpret Arterial Blood Gas Analysis?
The aim of performing an arterial blood gas analysis is to diagnose and manage the oxygenation status and acid-base balance of the high-risk patients, as well as in the care of morbidly ill patients in the intensive care unit.
The physician studies the values of the vital parameters and in the context of the clinical setting and the signs and symptoms of the patient, determines whether the lungs and kidneys are functioning optimally. Abnormalities in the functioning of these two major organs can lead to impaired homeostasis of the body leading to acid-base disturbances.
Characteristics of acid-base disturbances
| Disorder | pH | Primary problem | Compensation |
| Metabolic acidosis | ↓ | ↓ in HCO3– | ↓ in PaCO2 |
| Metabolic alkalosis | ↑ | ↑ in HCO3– | ↑ in PaCO2 |
| Respiratory acidosis | ↓ | ↑ in PaCO2 | ↑ in [HCO3-] |
| Respiratory alkalosis | ↑ | ↓ in PaCO2 | ↓ in [HCO3-] |
What are the diseases that are related to acid-base disorders?
The diseases manifesting with acid-base disorders are as follows-Metabolic Acidosis
– Ketoacidosis (diabetic, alcoholic, starvation)
– Renal diseases (renal tubular disease, chronic kidney disease)
– Drug-induced (mild in most cases, but can be fatal rarely)
Metabolic Alkalosis
– Use of diuretics
– Volume depletion (as a result of severe vomiting or nasogastric suction or diarrhea)
– Ingestion of excessive amounts of antacids
– Steroid-induced disorders
– Endocrine disorders (include hyperaldosteronism and hypercortisolism).
Respiratory Acidosis
– Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
– Sleep disorders
– Depression of the central nervous system (CNS) or drug-induced respiratory depression
– Impaired ventilation is secondary to a neuromuscular disease.
Respiratory Alkalosis
– Hyperventilation secondary to CNS stimulation or stimulation of pulmonary receptors (due to infection, embolus or edema)
– Hypermetabolic states including pregnancy, hyperthyroidism, and sepsis
– Drug-induced respiratory failure
What are the limitations of Arterial Blood Gas Analysis?
– The blood gas analysis cannot yield a specific diagnosis. A patient suffering from asthma may have the same findings as suffering from pneumonia.
– The analysis does not reflect the degree to which an abnormality affects a patient. A patient’s ability to compensate for the underlying abnormality can mask the findings.
– Blood gas analysis cannot be used as a screening test for early pulmonary disease. Severe disease may be present before significant changes are seen in blood gases.
What are the complications of Arterial Blood Gas Analysis?
– Pain at the site of arterial puncture
– Thrombosis, hematoma, hemorrhage
– Arterial embolism, arterial spasm, arterial insufficiency
– Infection
– Allergy to the local anesthetic used
– Pseudoaneurysm
– Compartment syndrome
– Vasovagal response.
What is the cost of Arterial Blood Gas Analysis in India?
The average cost of arterial blood gas analysis in India is ₹ 750.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2936733/
- https://www.thoracic.org/professionals/clinical-resources/critical-care/clinical-education/abgs.php
- https://anesth.unboundmedicine.com/anesthesia/view/Pocket-ICU-Management/534207/all/Interpretation_of_Arterial_Blood_Gases
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2058760-overview
Subscribe to free FactDr newsletters.
REVAMP YOUR
LIFE
HEALTH
WELLNESS
If you're enjoying our website, we promise you'll absolutely love our new posts. Be the first one to get a copy!
Get factually correct, actionable tips delivered straight to your inbox once a week.
We hate spam too. We will never share your email address with anyone. If you change your mind later, you can unsubscribe with just one click

By clicking Subscribe, I agree to the FactDr Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of FactDr subscriptions at any time.
Help Others Be Fit