Last Updated December 20th, 2021
Pneumonia – a deadly disease
In the recent years, viral and bacterial infections have become very common in tropical, sub-tropical, humid and temperate regions. These regions have the ideal weather and climatic conditions for the birth and spread of different pathogens. Respiratory diseases of viral or bacterial origin are becoming major public health issues globally. The most life-threatening disease of this category affecting children, teens, and adults worldwide at present is “pneumonia”.
According to epidemiological reports by the American Lung Association (2011), pneumonia is more prevalent in children below 5 years of age and leads to nearly 5 million deaths annually. Thus it is evident that global mortality and morbidity rates are getting significantly impacted by Pneumonia.
What is Pneumonia?
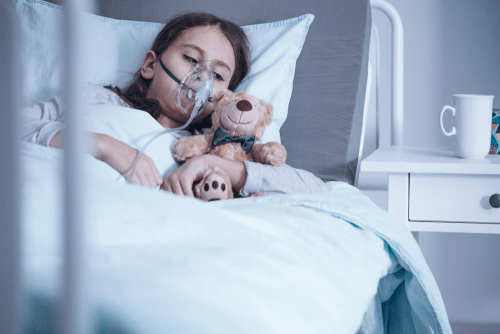
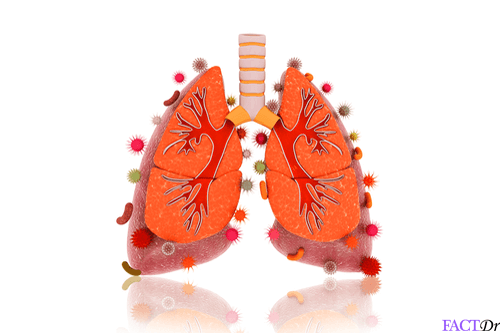
 Pneumonia is a respiratory disease in which acute inflammation of the lung tissues (lung parenchyma) occurs due to infections caused by viral or bacterial agents.
Pneumonia is a respiratory disease in which acute inflammation of the lung tissues (lung parenchyma) occurs due to infections caused by viral or bacterial agents.
In this condition infection, blockage and inflammation of the bronchi, lung alveoli (becomes filled with pus and fluid) and other parts of the respiratory tract normally occurs which leads to impaired functioning of the lungs, resulting in acute respiratory disorders such as a cough (productive or non-productive) and breathing ailments accompanied by fever.
The term Pneumonia is also used for few other interstitial, non-infectious lung diseases. A recent survey by the World Health Organization reveals that about 15% fatalities under 5 years of age were reported due to Pneumonia causing 920136 deaths in the year 2015.
Causes of Pneumonia
Pneumonia is mainly caused due to infection induced by viral or bacterial pathogens. But few other factors may also account for Pneumonia in adults and children. The generalized etiological factors behind Pneumonia are listed below-
- Bacterial infections: Infections caused by various bacterial species such as Pneumococcus, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus can cause bacterial pneumonia (lobar or broncho-lobular pneumonia). Acute infection may lead to pleural effusion, empyema, lung abscess in certain cases.
- Viral infections: Infections triggered by few viruses such as Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), Parainfluenza virus, Adenovirus account for 30-67% cases of pneumonia (source: American Lung Association). Primary and secondary lung abscesses may occur in critical cases.
- Fungal infections: Fungus found in soil or debris can cause Pneumonia in people with weak immune systems.
- Smoking: Increase in tobacco concentration within the body (caused due to active or passive smoking) predisposes the body to bronchial infections. Habitual smokers often develop emphysema, a respiratory disease where lung alveoli become dilated and are severely damaged. These factors can collectively contribute to Pneumonia.
- Industrial pollution: Particulates generated due to industrial emissions cause irritation and blocking of bronchial channels. Prolonged exposure to airborne irritants can cause chronic bronchial spasms accompanied by excessive mucus secretion (leading to edema and bronchial pneumonia).
- Lung diseases: In a few cases, patients suffer from bronchitis because of prevailing respiratory ailments like influenza, asthma, emphysema.
- Existing clinical conditions like seizure or stroke can lead to the accidental transfer of large volumes of food and gastric juice from the stomach to the lungs that causes aspiration pneumonia.
- Foreign materials present anywhere inside the respiratory tract can lead to aspiration pneumonia.
Transmission mediums of Pneumonia
 Pneumonia is highly contagious and can spread via the following routes –
Pneumonia is highly contagious and can spread via the following routes –
- Respiratory droplets acquired via coughing or sneezing
- Throat secretions of the patient that contains the viruses or bacteria
- Common items of use such as bed-sheets, utensils, towels etc
- Touching objects used by Pneumonia patients without washing hands.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
Pneumonia results in acute respiratory disorders which are manifested via the following symptoms-
- Productive ( with mucous discharge ) or a non-productive cough
- Acute breathlessness (dyspnea caused due to blockage of respiratory passage) accompanied by rapid breathing
- Discomfort and pain in the chest (especially during breathing or coughing)
- Rapid heart rate
- High fever with occasional chills and constant shivering
- Production of brownish or reddish mucous (due to the presence of blood)
- Profuse sweating
- Extreme fatigue
- Mental instability ( after a prolonged period of sickness)
- Thoracic pain
- Abdominal pain ( originally generated at diaphragm)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Persistent fever
- Pale and toxic appearance
- Sluggishness and inability to perform mundane activities like walking, running, climbing stairs, light physical exercise
- Dizziness
- Gastrointestinal disorders (in the advanced stage)
Types of Pneumonia
 Pneumonia can be classified either based on the source of origin or the medium of origin. The American Lung Association classifies Pneumonia into the following categories based on the source of origin –
Pneumonia can be classified either based on the source of origin or the medium of origin. The American Lung Association classifies Pneumonia into the following categories based on the source of origin –
Bacterial Pneumonia: Bacterial Pneumonia severely attacks the lung parenchyma and damages one or both the lungs. Depending on the portion of the lung parenchyma involved, bacterial pneumonia can be subdivided into two types-
- Lobar Pneumonia: Lobar Pneumonia is induced by different bacterial species such as Streptococcus, Staphylococcus or Pneumococcus. It affects the portion of the lobe, the whole lobe or both lobes of one or both lungs. It progresses in four distinct stages – the congestion stage, red hepatization stage, grey hepatization stage.
- Bronchopneumonia (Lobular Pneumonia): It is usually caused by Staphylococcus, Haemophilus, Pseudomonas or Coliform bacteria. It is characterized by reddish or grey patches in one or both lobes.
Viral Pneumonia: It is triggered by numerous viral species such as Cytomegalovirus, Parainfluenza virus, Rhinovirus or Adenovirus. It is characterized by inflammation of the interstitial lung tissues which affects the alveoli as well.
Based on the medium of the spread of Pneumonia, it can be classified into two types-
- Hospital- Acquired Pneumonia: It is a form of bacterial Pneumonia that is transmitted within a patient’s body within 48-72 hours of hospitalization.
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia: It refers to the form of Pneumonia acquired outside of hospitals or clinics.
Diagnosis
Chest X-ray is recommended in the first place to detect which part of the lung is affected and presence of accumulated fluids in lungs. Blood cultures and sputum cultures can be carried out to determine the degree of infection.
Treatment & Prevention
The most effective way to protect against the flu is to get the yearly influenza vaccine. These vaccines are specifically designed against Influenza A (H1N1, H3N2) and Influenza B virus. The population which is most vulnerable to flu infection comprises of children, pregnant women, diabetic patients, cardiac patients, and elderly people. People working in the healthcare sector are also exposed more to the pathogens. They MUST get the required vaccination. Your immune system resides in your gut. To build up your immunity naturally, you need to consume immunity-boosting foods such as citrus fruits, ginger extract, onions and garlic, and wholesome chicken soup. Sugar suppresses your immunity by destroying your gut’s bacteria culture. Avoid sugary treats and sweet food items in order to boost your immunity.
TL;DR?
Dos and Don'ts
- Drink plenty of fluids and eat only fresh fruits (non-sweet) and vegetables.
- Consume garlic, ginger, onions, and peppers as they fight disease-causing microbes.
- Maintain good hygiene. Stay indoors and avoid spreading the infection.
- Consume sugary foods or sweet fruits.
- Indulge in smoking or expose yourself to lung-irritants.
- Resort to self-medication or take over-the-counter drugs to treat the symptoms.
Help Others Be Fit
Related Conditions
Trending Topics