Last Updated December 20th, 2021
Overview of enlarged liver
The liver is the largest internal organ of the human body. It is responsible for diverse functions such as cholesterol metabolism, glycogen storage, hormonal balance, protein synthesis and purification of blood. Numerous problems of the liver may arise due to unhealthy dietary habits, addictive habits, and an unhygienic lifestyle. The most common form of liver disease is “Enlarged liver”. It is more prevalent in alcoholics. These people may develop Liver Cirrhosis and Fatty Liver disease in future. Enlarged liver is also common in infants suffering from hepatic diseases, particularly jaundice.
The World Health Organisation reports of 2010 show that nearly 1.4 million deaths were documented all over the world due to Hepatitis. An alarming statistics by the American Liver Foundation in the year 2016 has revealed that around 6 million children worldwide suffer from different types of liver diseases. Enlarged liver, in particular, is an extremely threatening condition. It may be an indicator of liver cancer and may even lead to death.
What is enlarged liver?
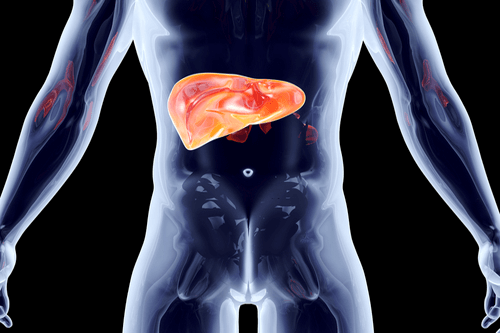 Enlarged liver or “Hepatomegaly” is an abnormal pathological condition in which the liver becomes unusually bigger than the normal size. This condition may arise due to some existing diseases (particularly liver disease) and a few unhealthy habits, such as alcoholism. Size of a healthy liver is 1.4-1.5 kg in men and 1.2-1.4 kg in women. The width of the liver is less than 16 cm along the mid-clavicular line. Abnormalities in any of the above measurements may be observed in a patient with an enlarged liver. An enlarged liver usually pushes down towards the Left Iliac Fossa (LIF). Enlarged liver is most commonly observed in patients with an alcoholic liver disease, liver cancer, or congestive cardiac failure.
Enlarged liver or “Hepatomegaly” is an abnormal pathological condition in which the liver becomes unusually bigger than the normal size. This condition may arise due to some existing diseases (particularly liver disease) and a few unhealthy habits, such as alcoholism. Size of a healthy liver is 1.4-1.5 kg in men and 1.2-1.4 kg in women. The width of the liver is less than 16 cm along the mid-clavicular line. Abnormalities in any of the above measurements may be observed in a patient with an enlarged liver. An enlarged liver usually pushes down towards the Left Iliac Fossa (LIF). Enlarged liver is most commonly observed in patients with an alcoholic liver disease, liver cancer, or congestive cardiac failure.
What causes enlarged liver?
Enlarged liver is attributed to a wide range of factors. The commonly studied causes are given below-
- Infections: Infections caused by viral or bacterial agents may lead to enlarged liver. A few examples of this category are- Viral Hepatitis (caused by the Hepatitis A, B or C virus), Mononucleosis (caused by the Epstein-Barr virus), Helminthic infection, Malaria or infection by Cytomegalovirus. People suffering from amoebic abscess or pyogenic abscess are also highly susceptible to enlarged liver condition.
- Auto-immune diseases: A few auto-immune liver diseases damage the liver cells permanently and give rise to an enlarged liver.
- Biliary diseases: Obstruction of the bile duct may occur due to certain existing biliary diseases like- Primary Biliary Cirrhosis, Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis, Cholangiocarcinoma and Pancreatic cancer. All of these diseases disrupt the normal mechanism of bile flow. This leads to the formation of an enlarged liver.
- Congestive cardiac conditions: People suffering from different types of cardiovascular disorders often experience a few major congestive cardiac conditions such as- Congestive Cardiac Failure, Constrictive Pericarditis (due to abnormal constriction of blood vessels in the peripheral regions), Right Ventricular Failure (due to valve dysfunctions) or Budd Chiari syndrome (due to obstruction of hepatic veins). These conditions lead to deficient supply of oxygen to the liver, which therefore fails to function normally. This may be manifested as an enlarged liver.
- Haematological diseases: Certain diseases related to abnormalities in haemoglobin level such as Sickle cell disease, Haemolytic anaemia, Leukaemia, Myeloma and Thalassaemia can lead to shortage of oxygen supply to the liver. This can lead to liver enlargement in due course of time.
- Tumours: People suffering from a few diseases like- Primary Hepatic tumour, Secondary Carcinoma, Sarcoidosis, Lymphoma and Amyloidosis develop benign or malignant tumours which obstruct the hepatic pathway. This can cause enlarged liver.
- Metabolic diseases: There are a number of metabolic diseases like – Wilson’s disease, Haemochromatosis, Glycogen storage disease, Fatty liver syndrome (non-alcoholic) and Diabetes mellitus which adversely impact the normal functioning of the liver. This may result in enlarged liver.
- Medications: Toxicities induced by a number of over-the counter drugs such as- Amiodarone, Paracetamol, Macrolides and Statins can cause enlargement of the liver.
- Alcohol abuse: Chronic alcoholics usually develop diseases like- Fatty liver disease and Alcoholic Hepatitis. Both the diseases may lead to an enlarged liver.
- Past infections: A history of recurrent liver diseases may cause permanent enlargement of the liver.
Symptoms of enlarged liver
 Signs and symptoms of enlarged liver are not so prominent in the early stages. In the more advanced stages, the following symptoms may be observed-
Signs and symptoms of enlarged liver are not so prominent in the early stages. In the more advanced stages, the following symptoms may be observed-
- Liver size greater than 3.5 cm below the right coastal margin (in infants)
- Rubbery or leathery texture of the liver surface (occurs in Hepatitis)
- Increased tenderness of liver ( in acute Hepatitis and venous congestion)
- Abnormal toughness and firmness of liver (in case of Cirrhosis)
- Formation of nodules on the liver (Hepatic cancer)
- Increased respiratory rate
- Fatigue
- Jaundice-like symptoms
- Spleen enlargement
- Increased bruising
- Dizziness
- Gastrointestinal disorders
- Fever
Types of enlarged liver
Enlarged liver conditions are broadly classified into two types depending on the texture of the liver surface-
- Smooth Hepatomegaly: In this condition, the liver surface is more or less smooth. Abnormal pulsation of the liver occurs in this condition. This kind of Hepatomegaly is observed in- Chronic heart failure, Hepatitis, early cirrhosis and tricuspid incompetence.
- Craggy Hepatomegaly: This form of Hepatomegaly is characterized by a rough texture of the liver surface due to the formation of nodules and tumours. This kind of Hepatomegaly is common in patients suffering from Primary Hepatoma or Secondary Tumours.
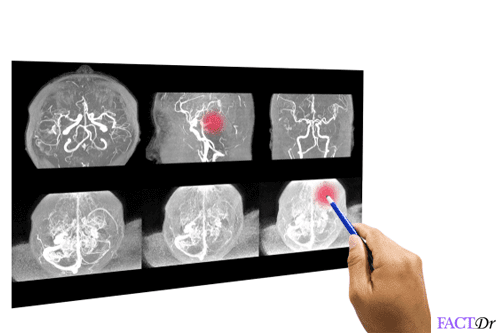
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of enlarged liver is very important for the determination of the exact cause. The following laboratory examinations are usually recommended by the doctors-
- Blood test (complete blood count)
- Fasting blood glucose
- Urinalysis
- Hepatitis serology
- Total and direct bilirubin
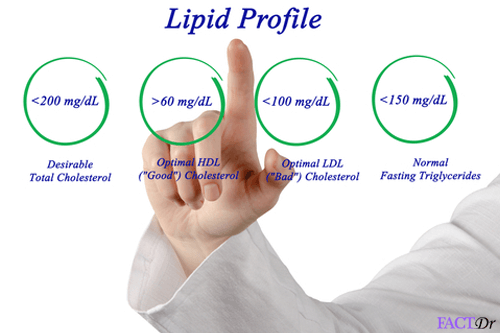
- Lipid profile
- Biopsy of liver
- Bone marrow aspiration
Treatment & Prevention
 The treatment for an enlarged liver depends on the exact cause or the underlying medical condition that is causing hepatomegaly. If the underlying condition is alcoholic hepatitis or non-alcoholic liver disease, substantial dietary and lifestyle changes can help the patient. This includes a strict limitation on alcohol consumption and fatty foods. If the liver enlargement is caused by a hepatitis infection, treating the infection and maintaining a careful diet can help reduce the symptoms.
The treatment for an enlarged liver depends on the exact cause or the underlying medical condition that is causing hepatomegaly. If the underlying condition is alcoholic hepatitis or non-alcoholic liver disease, substantial dietary and lifestyle changes can help the patient. This includes a strict limitation on alcohol consumption and fatty foods. If the liver enlargement is caused by a hepatitis infection, treating the infection and maintaining a careful diet can help reduce the symptoms.
Preventing any liver disorder includes the following measures:
- Consume more of fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains instead of greasy foods and sugar-laden items.
- Strict no-no to alcohol and smoking. Steer clear from any form of substance abuse.
- Always refer to a doctor before taking any medication, even if it’s OTC.
- Don’t expose yourself to harmful chemicals and toxic fumes. Limit your exposure to environmental toxins.
Dos and Don'ts
- Take get fully vaccinated for hepatitis B. Hepatitis B is responsible for almost 1/3rd of all cases of liver cirrhosis cases across the globe.
- Follow a well-balanced diet that eliminates excess fats, sugar, and preservatives.
- Keep a close monitor of your blood sugar, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. More so, if one has a family history of liver diseases.
- Resort to self-medication. Even non-prescription drugs, when taken in excess or unnecessarily, can damage the liver.
- Eat junk foods and foods which are stripped off nutrients and filled with trans-fats, artificial preservatives, and sugar.
- Indulge in illicit drug use. Also, refrain from sharing needles as this is one of the leading causes of hepatitis C.
Help Others Be Fit
Related Conditions
Trending Topics