Last Updated December 20th, 2021
Overview
Blood makes up about 7-8% of the body weight and is significant for the functioning of different organs in the body. This implies if something goes wrong with the blood, the functioning of more than one organ is negatively impacted causing adverse side-effects to one’s health. The preventive measures can be implemented to reduce the symptoms and complications of blood disorders to an extent, but despite that many can be fatal. Blood disorders can affect men, women, and children equally.
Definition of blood disorders
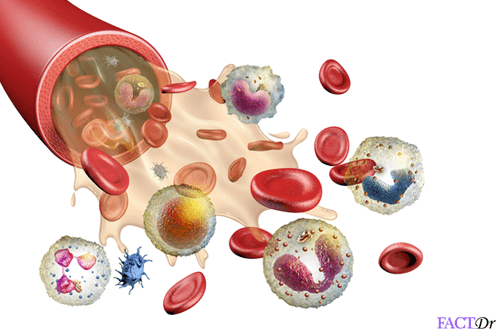
 When any of the main components of the blood, red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), plasma and platelets, have noticeable abnormalities, they cause a blood disorder or hematologic disorder. Examples of blood disorders: Leukemia, lymphoma, thalassemia, amyloidosis and many more.
When any of the main components of the blood, red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), plasma and platelets, have noticeable abnormalities, they cause a blood disorder or hematologic disorder. Examples of blood disorders: Leukemia, lymphoma, thalassemia, amyloidosis and many more.
Red blood cells: Help in the transport of oxygen to different parts of the body
White blood cells: Cells that form the immune system and help fight infections in the body
Platelets: Fuels the clotting of the blood to prevent bleeding
Plasma: The liquid part of the blood that remains if the RBCs, WBCs, platelets and other cellular constituents are removed
What causes blood disorders?
There are numerous blood disorders and each has different causes. But the general causes of blood disorders are an unhealthy diet, genetics and various diseases and infections. Blood disorders can also occur as a side-effect of medication.
Symptoms of blood disorders
Since the blood transports different nutrients throughout the body and helps in the functioning of different organs, symptoms of blood disorder are seen in different areas of the body. The symptoms are different for different abnormalities in the blood components.
Symptoms when there is a decrease in blood components
- Anemia
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Breathlessness
- Abrupt weight loss
- Nosebleeds
- Bleeding of gums
- Frequent and prolonged fever
- Injuries don’t heal as quickly as normal
Symptoms when there is an increase in blood components
- Excessive clotting of blood
- A frequent headache
- Red complexion
Types of binge blood disorders
 Blood disorders can be acute or chronic. Acute blood disorders occur abruptly and last for a short period of time. Chronic blood disorders develop slowly over a long period of time and hence, last longer. Roughly classified, blood disorders are of three types. Disorders of each type are caused because of the increase of decrease in cell count.
Blood disorders can be acute or chronic. Acute blood disorders occur abruptly and last for a short period of time. Chronic blood disorders develop slowly over a long period of time and hence, last longer. Roughly classified, blood disorders are of three types. Disorders of each type are caused because of the increase of decrease in cell count.
- Red Blood Cells Disorder:
- Increase in cell count – Erythrocytosis– Blood becomes too thick and so ease of flow is affected
- A decrease in cell count – Anemia – Lack of iron in the body
- White Blood Cells Disorder:
- Increase in cell count – Leukocytosis– Disorder related to neutrophils and lymphocytes erupt
- The decrease in cell count – Leukopenia – Makes people more prone to infections
- Platelets Disorder:
- Increase in cell count – Thrombocythemia– Abnormal blood clotting
- A decrease in cell count – Thrombocytopenia –Bleeding disorders
- Blood Plasma Disorder: Blood clotting and hemoglobin-related disorders.
Long-term effects of blood disorders
Blood is required for the functioning and survival of all the organs that compromise the body. Any disorders in the blood can cause adverse effects to the vital organs and most cannot be cured. However, once treated, the symptoms turn mild and complications are reduced.
Vulnerable groups
Those with an unhealthy diet and lifestyle and those whose relative has been diagnosed with a blood disorder are at a high risk of being affected with a blood disorder.
Genetics of blood disorders
Blood disorders are genetically transferrable diseases and genetics is one of the chief causes of being diagnosed with blood disorders. Blood clotting disorder, anemia, thalassemia and more are all genetically inherited diseases.
Diagnosis
 Physical procedures are first done where the doctor check for enlargement of different lymph nodes and unexplained blood clots. Needless to say, blood disorders are also diagnosed by blood tests. Different components of the blood are checked and cell counts recorded.
Physical procedures are first done where the doctor check for enlargement of different lymph nodes and unexplained blood clots. Needless to say, blood disorders are also diagnosed by blood tests. Different components of the blood are checked and cell counts recorded.
- RBC, WBC, and platelet cell count is examined
- Different proteins present in the blood
- Amount of hemoglobin present in RBCs.
Treatment and prevention
Anemia
Treatment
- If the cause of anemia is due to the lack of iron in the body, iron-rich foods will be added to the diet. If it caused due to loss of blood, then the cause of the bleeding needs to be found and taken care of.
- If the cause of anemia is due to the lack of vitamins in the body, folic acid, and B-12 rich foods will be added to the diet. If the body is unable to absorb B-12 from food, vitamin B-12 will be injected into the body; this treatment method may continue for the duration that the body cannot absorb B-12 via food.
- To treat anemia caused due to chronic diseases, doctors will treat the underlying cause. A blood transfusion or injection of the hormone erythropoietin (produced in the kidney) will be given, to help in increasing the production of the red blood cells.
- To treat aplastic anemia doctors will recommend a blood transfusion or a bone marrow transplant to increase the count of the red blood cells in the body.
- In cases where anemia is caused due to bone marrow diseases, the doctor will look at the current medications that the patient is on, how well chemotherapy worked on the patient or if the patient is ready for chemotherapy and a bone transplant. This helps in monitoring the progress of the treatment on the condition.
- In cases of hemolytic anemia, triggers causing a reduction in the RBC’s will be monitored along with medications to suppress the immune system will be prescribed to make sure that they do not attack the healthy red blood cells. At times, a blood transfusion may be needed or a plasmapheresis (the process filtering blood) may be required to make sure that the red blood cells level in the body remains constant and on a normal level.
- Anemia caused due to sickle cells will be treated by administering oxygen and medications to relieve pain. In severe cases, a blood transfusion, folic acid supplements, and antibiotics may be provided to reduce the pain and treat the condition. At times, a cancer drug called hydroxyurea is prescribed to treat this form of anemia.
Prevention
- Consume iron rich food.
- Consume foods rich in folate.
- Consumption of vitamin B-12, directly or consume supplements.
- Consume vitamin C, directly or use supplements.
Thalassemia
Treatment
- Those who have been diagnosed with mild thalassemia will need blood transfusions occasionally.
- Those who have been diagnosed with severe thalassemia will need a recurrent blood transfusion. Since recurrent blood transfusion increases the iron levels in the body, drugs to reduce the iron level in the body will be prescribed as well.
- A stem cell transplant also called a bone marrow transplant may be recommended to certain patients to ensure that they do not need recurrent blood transfusions.
Prevention – There are no sure shot prevention methods for thalassemia as it is a genetic condition.
Thrombocythemia
Treatment
- Those who have been diagnosed with thrombocythemia will be prescribed a low dosage of over-the-counter medications to reduce the blood clot levels in their body.
- Certain medications to reduce the production of platelets in the bone marrow will be prescribed.
- A surgical procedure to remove the platelets from the bone marrow will be conducted.
Prevention
- Control medical condition such as diabetes and blood pressure.
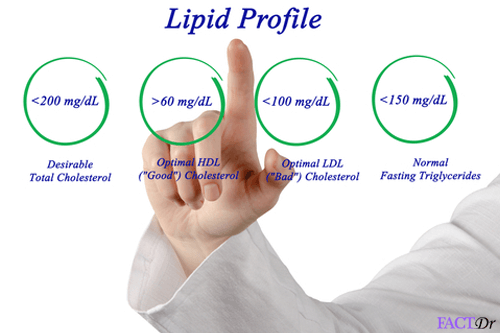
- Monitor cholesterol levels.
- Exercise regularly.
- Quit smoking.
Leukocytosis
Treatment
- Those who have been diagnosed with leukocytosis will require additional fluids in their blood vessels, these are provided intravenously.
- Antibiotics, steroids, antacids and anti-uric acid medications are provided to those who have been diagnosed with leukocytosis to help reduce the chances of infections, reduce inflammation, reduce the urine levels in the kidney and reduce the levels of uric acid in the body.
- Patients with leukocytosis are treated by removing blood from their body using a platelet apheresis machine. This machine is also used to circulate the remaining blood in the body.
- In certain cases, patients will undergo chemotherapy to kill off the cancerous blood cells in the body along with a few healthy ones. The remaining healthy WBC’s will continue to circulate through the body.
- A complete or partial blood transfusion will be done to treat leukocytosis.
- Those who have been diagnosed with leukocytosis may need a bone marrow transplant to replace the damaged bone marrow with a healthy one.
Prevention
- Avoid consuming artificial sweeteners, processed food, and oily foods.
- Add omega-3 to your diet.
- Stop smoking.
- Do not consume excessive amounts of alcohol.
- Include vitamins, minerals, and nutrients to your diet.
Blood Disorders Home Remedies
Home remedies for curing anemia
- Vitamin C rich foods such as lemon and oranges as these help in absorption of iron.
- Yogurt with turmeric is a traditional Ayurvedic remedy for anemia.
- Green leafy vegetables such as spinach and mustard greens are rich sources of iron.
- Fresh juice of pomegranate or beetroot is rich in folic acid, iron, and potassium – these not only alleviate anemia symptoms but also increase energy levels.
- Soaked black sesame seeds are also abundant in iron.
Natural blood thinners
- Turmeric and ginger – both these natural remedies have anti-coagulating and anti-inflammatory properties and thus prevent thickening and clotting of blood.
- Foods that are rich in vitamin E reduce blood clotting. It is found abundantly in almonds, sunflower oil, wheat germ oil, and whole grains.
- Garlic also has strong anti-coagulating properties. Chewing one raw garlic pod in empty stomach can keep circulation strong along with improving your cardiac health.
TL;DR?
Dos and Don'ts
- Eat home-made foods, this measure helps in strengthening the immune system.
- Consume small and more frequent meals, this helps in maintaining the blood sugar levels.
- Take caution when you are taking vitamins if you are already on certain medications, this helps in avoiding complications.
- Indulge in smoking; this habit tends to increase the number and frequency of internal blood clots.
- Consume excessive alcohol. This is because alcohol tends to destroy the red blood cells (RBC’s)
- Consume coffee or tea along with your vitamins, as they tend to destroy the nutritional value of the vitamins.
Help Others Be Fit
Related Conditions
Trending Topics