Last Updated December 20th, 2021
Overview of genetic diseases
In the recent years, the statistics of Global Genes have shown that there are nearly 7000 rare diseases in the world and an estimated 300 million people live with those diseases. They have also established the fact that 6% of the babies are born with rare genetic diseases and about 30% of them die before the age of five. Extensive research works have proved that majority of these diseases are caused by genetic mutations and are unpredictable in most cases. These diseases typically run in the families and are usually present at birth. On various occasions, these are triggered and aggravated by environmental factors as well.
Not all genetic diseases are fatal. But most of them are debilitating in nature. The global health organizations are arranging campaigns to spread the awareness related to these diseases in a bid to reduce the current global burden of genetic disorders.
What are genetic diseases?
Genetic diseases are the rare diseases that arise from mutations in a single or multiple genes. The possibility of occurrence of these diseases in the future generations depends on whether the dominant or the recessive gene is expressed in the immediate generation. These diseases are mainly fatal and even if the people survive that suffer from some of the other forms of disability. Most of these diseases are present from birth and are therefore known as congenital disorders. In a few cases, the disease expresses itself within one year of birth. These children need special aids to lead their lives like normal people.
Till date, nearly 4000 rare genetic diseases have been identified and the research groups affirm that more diseases of this category will be discovered in the upcoming years. It is worth mentioning in this context that autoimmune disorders or immune system disorders that affect a large section of the global population also fall into the category of genetic diseases.
What are the different types of genetic diseases?
 Genetic diseases may be classified into two broad categories namely single-gene disorder and multi-gene disorder. They have further sub-categories. These are discussed below-
Genetic diseases may be classified into two broad categories namely single-gene disorder and multi-gene disorder. They have further sub-categories. These are discussed below-
Single-gene disorders: As the name implies, single gene disorders result from the mutation of a single gene. Diseases occurring due to single gene mutation can be passed on to the future generations in a number of ways. But in every case, this transmission is affected by uniparental disomy and genomic imprinting, which is expressed in the inheritance patterns. Single gene disorders may be of the following types-
- Autosomal dominant: Only one mutated copy of the gene is involved in this disease. Only one of the parents is affected by the disease. The probability of the child inheriting the mutated gene is 50% in this disease. There are many instances where the child does not have the disease even after inheriting the gene. The commonly known examples of this disease are- Huntington’s disease, Marfan syndrome, Tuberous sclerosis etc.
- Autosomal recessive: In this case, two copies of the mutated gene are necessary for the child to inherit the disease. None of the parents are affected by the disease, but each carries a single copy of the defective gene. The chance of the child having the disease is 25%. Some examples of this type of genetic disease are Albinism, Roberts syndrome, Sickle cell disease, Cystic fibrosis and Niemann-Pick disease.
- X-linked dominant: These diseases occur due to mutations in the genes of the X chromosome. This is an extremely rare variety of genetic disease and is more likely to be observed in males. A few examples are- Rett syndrome and Aicardi syndrome.
- X-linked recessive: These are also caused by the mutations in the genes on the X chromosomes. In this disease also, the males are more likely to get affected than the females. A woman carrying an X-linked recessive gene has a 50% chance of having sons who are affected and a 50% chance of having daughters who are the carriers of a single copy of the mutated gene. The common diseases, in this case, are- male pattern baldness, color blindness, Hemophilia A and Lesch-Nyhan syndrome.
- Y-linked: These are caused by mutations on the Y chromosome and are also called holandric disorders.
- Mitochondrial: Mutations in the genes of the mitochondrial DNA cause these disorders.
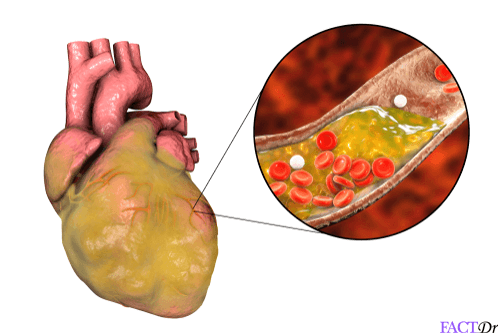
- Multi-gene disorders: These are also called polygenic diseases and are caused by the effects of multiple genes, combined with environmental factors and lifestyle trends. These include some of the common familial diseases like – asthma, cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, bowel diseases etc.
Some common genetic diseases
 This section will present a discussion of some of the commonly studied genetic diseases. Given below is a detailed list of such diseases-
This section will present a discussion of some of the commonly studied genetic diseases. Given below is a detailed list of such diseases-
- Down syndrome: It is also called Trisomy 21 and occurs due to the presence of a third copy of chromosome 21. The patients exhibit abnormal facial patterns, retarded growth, and cognitive disabilities.
- Cystic fibrosis: This mainly affects the lungs. The patients suffer from chronic pulmonary disorders.
- Huntington’s disease: Here the patients exhibit lack of coordination and an abnormal and unstable gait. It finally culminates in the death of the brain cells.
- Sickle-cell disease: In this case, the patients inherit two defective copies of the hemoglobin gene. This category normally comprises a group of blood disorders.
- Hemophilia: It is a genetic disease where the patients lack blood coagulation capacity.
- Fragile X syndrome: It is a rare genetic disease which is mainly marked by intellectual disabilities and defective facial patterns.
Diagnosis and treatment
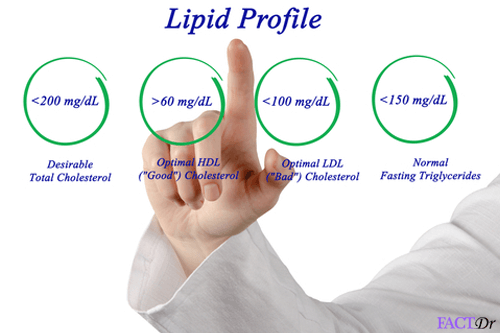
 Prenatal diagnosis can detect many of the genetic diseases in the gestation period itself. The most common technique followed by the doctors, in this case, is Amniocentesis, which is basically an invasive technique. Blood tests such as triple marker blood test are also used to accurately diagnose the presence of genetic abnormalities in the fetus.
Prenatal diagnosis can detect many of the genetic diseases in the gestation period itself. The most common technique followed by the doctors, in this case, is Amniocentesis, which is basically an invasive technique. Blood tests such as triple marker blood test are also used to accurately diagnose the presence of genetic abnormalities in the fetus.
The treatment techniques of genetic diseases are still under research. In some countries, innovative genetic treatments have been devised which are facilitating the birth of a healthy baby.
The treatment plan for a genetic disorder is formulated focusing on the improvement of the signs and symptoms. The treatment varies from individual to individual based on the condition and its severity. For instance, a bone marrow transplant might be required in case of sickle cell anemia, a genetic disorder resulting in a heart defect is treated by a surgery or a heart transplant.
Prevention of the genetic diseases is mainly by keeping a record of your family history. Genetic testing before conception (prenatal testing) and screening the newborn can play a vital role in the prevention of the disease and increase awareness about the possibilities.
Pre-symptomatic or predictive testing can help in diagnosing a disease which runs in the family even before the appearance of the symptoms. Pre-implantation testing screens the embryo for genetic abnormalities when an attempt is made to conceive a child through in vitro fertilization. The healthy embryos (without any genetic abnormalities) are implanted in the uterus in hopes of achieving pregnancy.
- http://www.who.int/genomics/public/geneticdiseases/en/index2.html
- https://www.cdc.gov/genomics/famhistory/famhist_basics.htm
- http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/congenital-anomalies
- https://www.healthline.com/health-news/test-your-newborns-dna-for-genetic-diseases#1
- https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/primer/consult/treatment
Dos and Don'ts
- If your family has a history of a particular kind of disease such as cancer, it becomes even more important to practice healthy lifestyle habits such as no smoking or alcohol consumption.
- Get yourself and your blood relatives screened for diseases which are genetically passed on in your family.
- If you have a family history of genetic disorders and are planning on starting a family, it is always wise to talk to a genetic counselor before conceiving.
- If your family member has a genetic disorder, it is important to equip yourself with all the information about the disease. The Internet can be helpful, but not all sources are authentic. It is better to join support groups for the long term.
- Encourage consanguineous marriages (marriages in close relatives) as they may cause the occurrence of recessive syndromes.
- Continue unhealthy lifestyle habits such as smoking, lack of physical activity, excess consumption of alcohol and processed meat etc.
Help Others Be Fit
Related Conditions
Trending Topics